Sexually transmitted infections
Gonorrhoea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which has progressively developed resistance to globally recommended treatments and has been identified by the World Health Organization as a priority infection urgently requiring new antibiotics. To address the lack of effective drugs, the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP) is developing a new treatment for gonorrhoea and is working to ensure it is available to everyone who needs it, wherever they live.
A new gonorrhoea treatment
GARDP is partnering with biotech Entasis Therapeutics on the development of a novel antibiotic called zoliflodacin. As a first-in-class treatment, zoliflodacin is active against resistant strains of gonorrhoea. Zoliflodacin has also been designed as an oral treatment option, which has the potential for significant benefits compared to the current standard of care of intramuscular injections. Following positive phase 2 results, the drug is currently being evaluated in a global phase 3 trial. The trial, which is assessing the effectiveness and safety of zoliflodacin against available gonorrhoea treatments, is underway in the United States, Netherlands, Thailand and South Africa.
Under its partnership agreement, GARDP is responsible for the phase 3 trial and pharmaceutical development activities for zoliflodacin to support regulatory approval and market access. GARDP will have commercial rights to zoliflodacin in all low- and middle-income countries. The zolifoldacin programme is a ground-breaking example of a public-private partnership approach to developing a novel antibiotic that prioritizes market access within countries that have high rates of gonorrhoea and for patients who need the treatment most. To learn more download the Partnership Overview document.
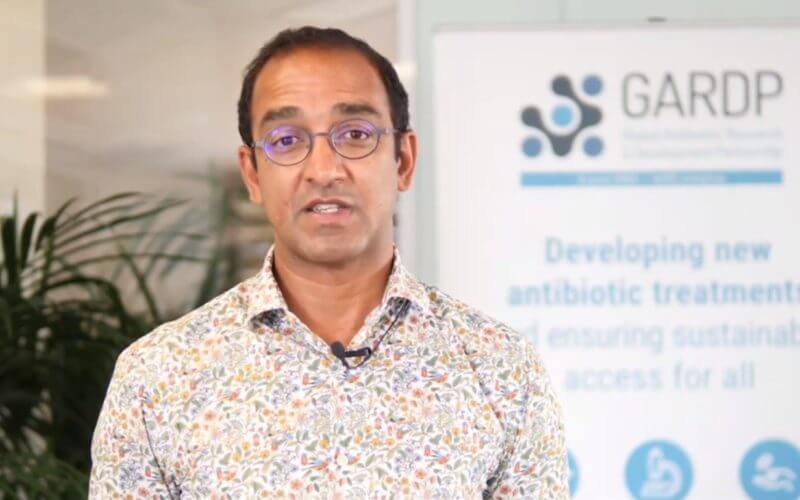
“The initiation of the phase 3 trial of zoliflodacin is an important milestone and brings hope for people affected by gonorrhoea. The global nature of the trial, across four continents, represents our commitment to ensuring this treatment is available to anyone who needs it, wherever they live.”
– Manica Balasegaram, Executive Director of GARDP
Warning: getimagesize(): https:// wrapper is disabled in the server configuration by allow_url_fopen=0 in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 46
Warning: getimagesize(https://old.gardp.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GARDP-gonorrhoea-phase-3-trial-alabama-page-tile.jpg): failed to open stream: no suitable wrapper could be found in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 46
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 46
Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to first-line antibiotics has increased rapidly in recent years and has reduced treatment options. In 2017-2018, in many countries, ciprofloxacin resistance was found to be exceedingly high, azithromycin resistance was increasing, and decreased susceptibility or resistance to ceftriaxone and cefixime continued to emerge. Download the sexually-transmitted infections programme In Focus to learn more about GARDP’s work to address drug-resistant gonorrhoea.
Warning: getimagesize(): https:// wrapper is disabled in the server configuration by allow_url_fopen=0 in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 40
Warning: getimagesize(https://old.gardp.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/consultation-doctor-tile.jpg): failed to open stream: no suitable wrapper could be found in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 40
Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/clients/c9b0ed6b0786a56afdaf5611fa7b11b2/web/old/wp-content/themes/gardp/template-parts/content-page-sections.php on line 40
While gonorrhoea can infect anyone, it disproportionately impacts women, who are less likely than men to have symptoms and thus seek care. Watch Dr Carolyn Deal, Chief of the STD Branch of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, discuss the impact of gonorrhoea on women’s health.
The rise of ‘super-gonorrhoea’
The gonorrhoea bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae can evolve to defeat the drugs designed to kill it. This process has been accelerated by the inappropriate use and overuse of antibiotics. Drug-resistant gonorrhoea has been reported in every region of the world, while some countries are finding ‘super-gonorrhoea’ infections that are untreatable by all available drugs. The WHO has called for urgent action to develop new antibiotics for gonorrhoea and is partnering with GARDP to support the development of a new treatment.
Evaluating an urgently needed treatment for gonorrhoea




